ASP.NET Core Attribute Routing

ASP.NET Core Attribute Routing adds routes by applying C# attributes on the controller and actions methods. Note that if convention routes are also present then we can override them by adding attribute routes. This is because DOT NET gives preference to attribute routes.
Page Contents
The concept of Routing is very vast and I have covered it in 6 tutorials which are:
- 1. Learn ASP.NET Core Convention-Based URL Routing
- 2. What is Endpoint Routing, Implementing it from start [with codes]
- 3. Learn ASP.NET Core Route Constraint in details with lots of examples
- 4. ASP.NET Core Attribute Routing
- 5. ASP.NET Core Routing Generating URLs
- 6. Areas and Routing in ASP.NET Core
So make sure you cover each of these one by one.
In Visual Studio create a new ASP.NET Core project by selecting the ASP.NET Core Web App (Model-View-Controller) template and name it AttributeRouting.
We can find the default convention route of the app in the Program.cs class for DOT NET 6.0 or in Startup.cs class for DOT NET 5.0 or earlier. See below given default route.
// In DOT NET 6.0
app.MapControllerRoute(
name: "default",
pattern: "{controller=Home}/{action=Index}/{id?}");
// In DOT NET 5.0 or earlier
app.UseEndpoints(endpoints =>
{
endpoints.MapControllerRoute(
name: "default",
pattern: "{controller=Home}/{action=Index}/{id?}");
});
How do I set attribute routing? We apply attribute routing through C# attribute called [Route()] on the controllers or action methods. For example apply the attribute – [Route("CallRoute")] to the Home Controller’s Index action method. This will add an attribute route for this action method. The url to initiate the Index action based on this route will be “/CallRoute”.
Check the below code where Attribute Route is applied and shown in highlighted manner.
using AttributeRouting.Models;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc;
using System.Diagnostics;
namespace AttributeRouting.Controllers
{
public class HomeController : Controller
{
[Route("CallRoute")]
public IActionResult Index()
{
return View();
}
// other actions
}
}
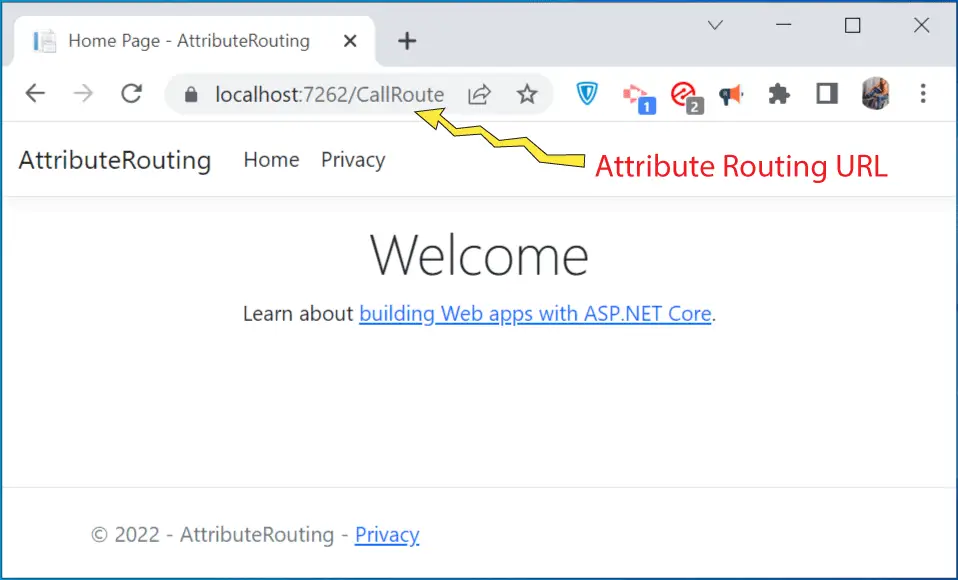
Now run your application and go to the URL – https://localhost:7262/CallRoute. We find the Index action method of the Home controller is invoked. This is because the string given on the Route attribute will become the URL for this action method.
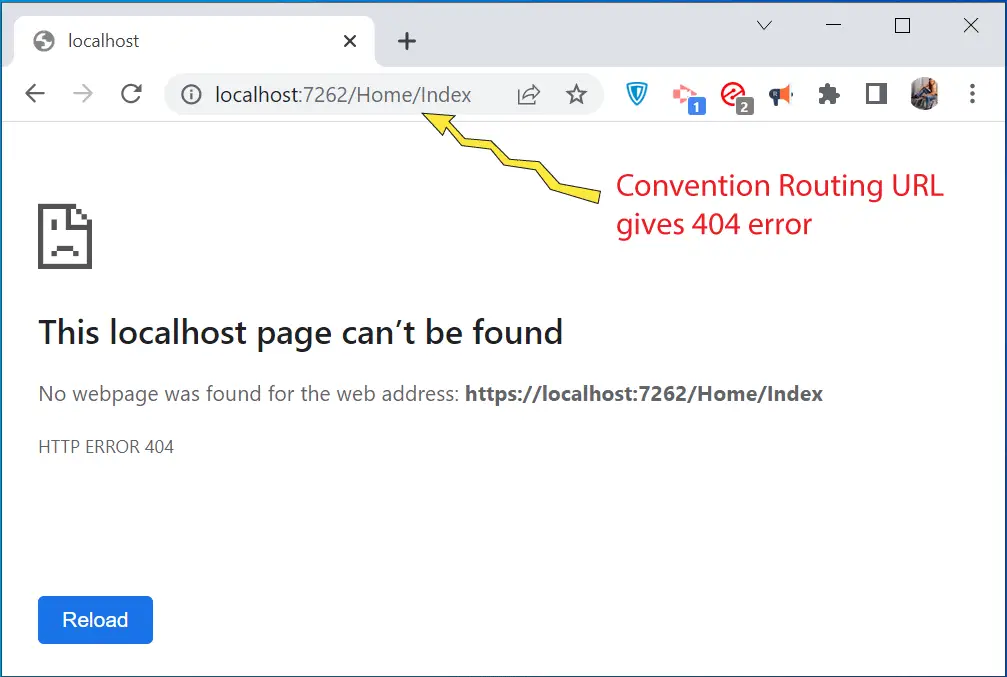
Now let’s open the Convention Routing based URL for this action method which is https://localhost:7262/Home/Index. We will see that this URL no longer works because attribute routing overrides convention routing and so old routes no longer works.
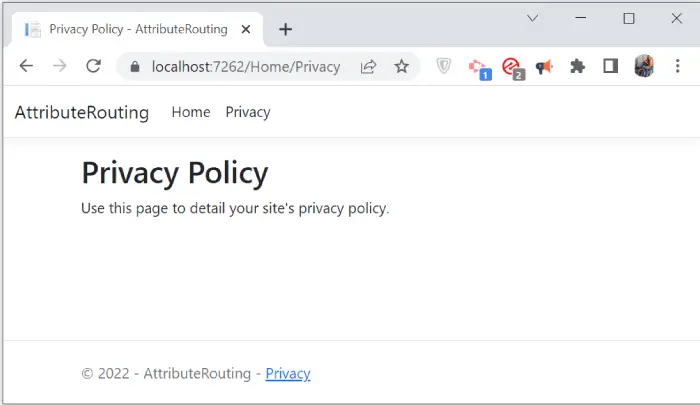
This is something which you should keep in mind when applying attribute routing. This does not means all Convention Routes will stop working. Only those will stop where both Convention and Attriube Routes are applicable as attribute routes take preference from ASP.NET Core. You can test this thing by opening the url – https://localhost:7262/Home/Privacy for the Privacy action of the same HomeController. This will open well on the browser.
The ‘controller’ & ‘action’ tokens in Attribute Routing
The [controller] and [action] tokens in an attribute route reference the Controller and Action names. To understand it create a new Controller and name it AdminController.cs. Add the following code to this controller:
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc;
namespace AttributeRouting.Controllers
{
public class AdminController : Controller
{
[Route("[controller]/CallMe")]
public string Index()
{
return "'Admin' Controller, 'Index' View";
}
public string List()
{
return "'Admin' Controller, 'List' View";
}
}
}
We applied the Attribute Route as C# attribute to the Index action method. This route has the term called controller which states that the URL should have the Controller segment in it. The controller segment value will be the controller name where this attribute route is place which is “Admin” controller. After it we have a string “CallMe”, so the URL for invoking this action method becomes – /Admin/CallMe.
Test it by running the app and opening the URL – https://localhost:7262/Admin/Callme. You will find Index action of Admin controller is invoked as shown by below image.
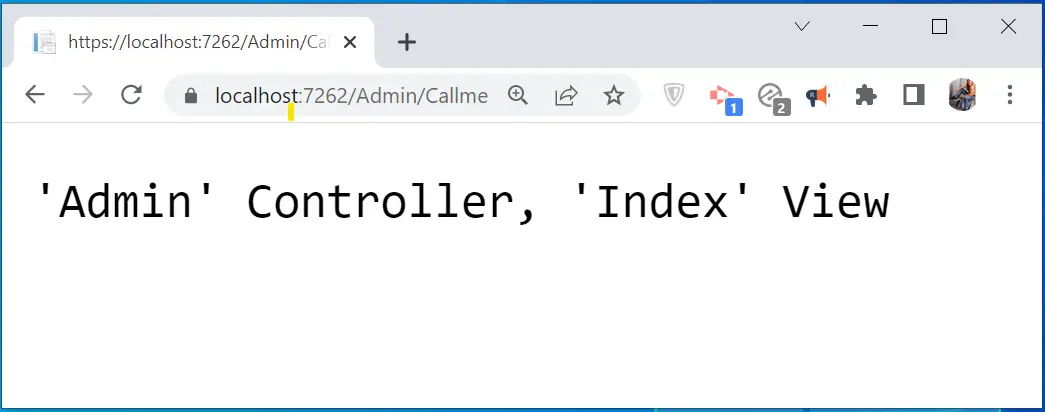
Note that since there is no Attribute Routes applied to the List action so it’s URL will be formed by the Convention Routing, and that will be https://localhost:7262/Admin/List.
Now we will see how Action token is applied on attribute routing. Add another action method called Show to the AdminController.cs and also apply attribute route to it as shown below:
[Route("[controller]/CallMe/[action]")]
public string Show()
{
return "'Admin' Controller, 'Show' View";
}To invoke this action the URL will be – https://localhost:7262/Admin/CallMe/Show
We can also apply attribute routing on the Controller. So all the action methods will inherit this route. Change the code of the Admin Controller as shown below:
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc;
namespace URLRouting.Controllers
{
[Route("News/[controller]/USA/[action]/{id?}")]
public class AdminController : Controller
{
public string Index()
{
return "'Admin' Controller, 'Index' View";
}
public string List(string id)
{
return "'Admin' Controller, 'List' View";
}
}
}
The Attribute Routing is applied to the Admin controller so both its action method inherit it.
Here the URLs to invoke Index action will be:
/News/Admin/USA/Index
/News/Admin/USA/Index/100
/News/Admin/USA/Index/HelloAnd the URLs to invoke List action will be:
/News/Admin/USA/List
/News/Admin/USA/List/100
/News/Admin/USA/List/HelloAttribute Routing Constraints
Route Constraints can be applied to the Attribute Routing just like convention routing. For example in the below code we applied Int Contraint for the “id” segment of the attribute route. This will allow only int values for the id segment.
[Route("[controller]/[action]/{id:int}")]
public class AdminController : Controller
{
}So in the above case the URLs which will match are:
/Admin/Index/10
/Admin/List/4
/Admin/Privacy/5The below URLs will not match.
/Admin/Index/Jack
/Admin/List
/Admin/Privacy/USA/100I created a Custom Route Constraint called OnlyGodsConstraint on my last tutorial. It can be applied to the attribute routing as well – just like what we did in the below highlighted code of the Admin controller:
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc;
namespace URLRouting.Controllers
{
[Route("News/[controller]/USA/[action]/{id:allowedgods?}")]
public class AdminController : Controller
{
public string Index()
{
return "'Admin' Controller, 'Index' View";
}
public string List(string id)
{
return "'Admin' Controller, 'List' View";
}
}
}
So the URL to invoke the Index method will become – https://localhost:7262/News/Admin/USA/Index/Shiv. See the below image:
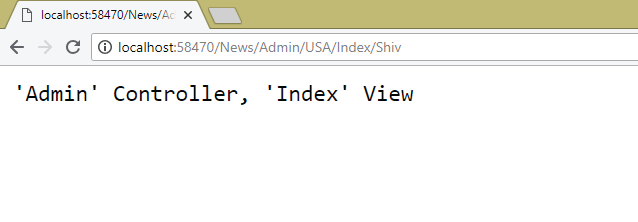
Download the full codes of this tutorial from the below link:
In this tutorial we learned to use Attribute-Based Routing. I hoped you liked this tutorial. Check the next tutorial whose link is given below.






 Welcome to YogiHosting - A Programming Tutorial Website. It is used by millions of people around the world to learn and explore about ASP.NET Core, Blazor, jQuery, JavaScript, Docker, Kubernetes and other topics.
Welcome to YogiHosting - A Programming Tutorial Website. It is used by millions of people around the world to learn and explore about ASP.NET Core, Blazor, jQuery, JavaScript, Docker, Kubernetes and other topics.