Globalization and Localization with Resource Files in ASP.NET Core

Page Contents
If you are working with Globalization & Localization feature of ASP.NET Core then resource files will always come into play. A resource file (.resx) is a useful mechanism for separating culture specific strings from code. These files contain key/values items and can be created from Visual Studio by selecting Add ➤ New Item in the solution explorer. For example, if your website has 3 supported cultures – French, Spanish, & English (English being the default culture) then you will have to create 2 types of resource files, i.e. for French and for Spanish.
In this tutorial I will show how to fetch and display localized culture based string from different areas of the website, these are:
- 1. Controllers using IStringLocalizer
object. - 2. Data Annotations error messages.
- 3. Custom Validation attribute error messages.
- 4. Views through IViewLocalizer object.
I will explain all this by creating a Multilingual Job Application form which will be based in 3 languages – English, French & Spanish.
This tutorial is a part of Globalization and Localization in ASP.NET Core. There are 3 tutorials to master it:
- 1. How to use Globalization and localization in ASP.NET Core
- 2. Globalization and Localization with Resource Files in ASP.NET Core
- 3. How to perform Localization with Portable Object (PO) files in an ASP.NET Core
Configurations in Program class
The first step is to tell the application which cultures your website will support, add the localisation services in your application, and do other necessary setups. So go to Program.cs and first add the below given 2 code lines:
builder.Services.AddControllersWithViews().AddViewLocalization(LanguageViewLocationExpanderFormat
.Suffix).AddDataAnnotationsLocalization();
builder.Services.Configure<RequestLocalizationOptions>(options =>
{
var supportedCultures = new[]
{
new CultureInfo("en-US"),
new CultureInfo("fr"),
new CultureInfo("es")
};
options.DefaultRequestCulture = new RequestCulture(culture: "en-US", uiCulture: "en-US");
options.SupportedCultures = supportedCultures;
options.SupportedUICultures = supportedCultures;
});These code lines tell 2 things:
- 1. You want Localization feature to be made ready for Data Annotations and Views.
- 2. Your site supports 3 cultures – ‘en-US’ (English – us), ‘fr’ (French) & ‘es’ (Spain). The ‘en-US’ being the default one.
Next, add the localization Middleware after the app.UseRouting(); code. This allow the use of Localisation Services in your application:
var locOptions = app.Services.GetService<IOptions<RequestLocalizationOptions>>();
app.UseRequestLocalization(locOptions.Value);You are now all set to use Globalization & Localization feature of ASP.NET Core and create a multi language job application form by using resource files.
DataAnnotations localization using Resource files
The first thing you do is create a model class for the job application form. Therefore create a new class inside the Models folder and name it JobApplication.cs. This class contains fields for Name of the applicant, email address, DOB, etc. Also, applied different attributes like [Required], [RegularExpression], [Range], [Display] to various fields.
The class full code is given below:
using System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations;
namespace GloLocR.Models
{
public class JobApplication
{
[Required(ErrorMessage = "Please provide your name")]
[Display(Name = "Job applicant name")]
public string Name { get; set; }
[RegularExpression("^[a-zA-Z0-9_\\.-]+@([a-zA-Z0-9-]+\\.)+[a-zA-Z]{2,6}$", ErrorMessage = "E-mail is not valid")]
[Display(Name = "Job applicant email")]
public string Email { get; set; }
[CustomDate]
[Display(Name = "Date of Birth")]
public DateTime DOB { get; set; }
[Required(ErrorMessage = "Please select your sex")]
[Display(Name = "Job applicant sex")]
public string Sex { get; set; }
[Range(2, 4, ErrorMessage = "{0} must be a number between {1} and {2}")]
[Display(Name = "Job applicant experience")]
public int Experience { get; set; }
[Range(typeof(bool), "true", "true", ErrorMessage = "You must accept the Terms")]
[Display(Name = "Terms")]
public bool TermsAccepted { get; set; }
}
}Next, create resource files to contain localized strings for these error messages and display names. So create 2 resource files in the same directory of the JobApplication.cs class i.e. inside the “Models” folder, and name them as:
- JobApplication.es.resx
- JobApplication.fr.resx
Note : See the names of the resource files where I have put ‘.es’ for Spanish one and ‘.fr’ for French.
In each of these resource files you have to add the strings (i.e. error messages and display name of the attributes) and their respective French and Spanish texts. Do this for each of the strings. I have shown this in the below 2 images of these 2 resource files.
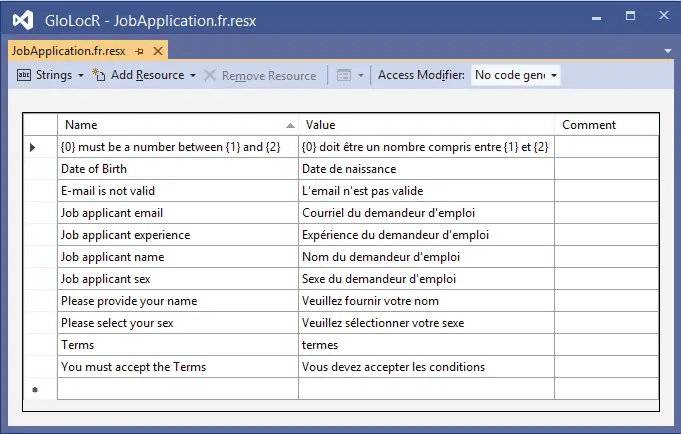
It’s enteries are given below:
| Name | Value |
|---|---|
| {0} must be a number between {1} and {2} | {0} doit être un nombre compris entre {1} et {2} |
| Date of Birth | Date de naissance |
| E-mail is not valid | L’email n’est pas valide |
| Job applicant email | Courriel du demandeur d’emploi |
| Job applicant experience | Expérience du demandeur d’emploi |
| Job applicant name | Expérience du demandeur d’emploi |
| Job applicant sex | Sexe du demandeur d’emploi |
| Please provide your name | Veuillez fournir votre nom |
| Please select your sex | Veuillez sélectionner votre sexe |
| Terms | termes |
| You must accept the Terms | Vous devez accepter les conditions |
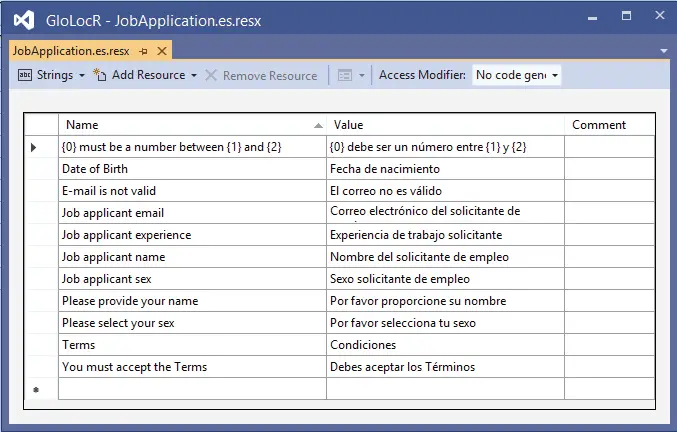
It’s enteries are given below:
| Name | Value |
|---|---|
| {0} must be a number between {1} and {2} | {0} debe ser un número entre {1} y {2} |
| Date of Birth | Fecha de nacimiento |
| E-mail is not valid | El correo no es válido |
| Job applicant email | Correo electrónico del solicitante de empleo |
| Job applicant experience | Experiencia de trabajo solicitante |
| Job applicant name | Nombre del solicitante de empleo |
| Job applicant sex | Sexo solicitante de empleo |
| Please provide your name | Por favor proporcione su nombre |
| Please select your sex | Por favor selecciona tu sexo |
| Terms | Condiciones |
| You must accept the Terms | Debes aceptar los Términos |
Custom Validation Localization Strings
I have created a custom validation attribute called [CustomDate] for data of birth field. In this I will perform my custom validation on the dob field of the applicant.
[CustomDate]
[Display(Name = "Date of Birth")]
public DateTime DOB { get; set; }So, create a new class called CustomDate.cs and place it inside a new folder called Infrastructure. You can name this folder anything based on your liking. Since this class is a custom validator so you have to inherit it from ValidationAttribute class. The full code of this class is given below:
using Microsoft.Extensions.Localization;
using System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations;
namespace GloLocR.Infrastructure
{
public class CustomDate : ValidationAttribute
{
protected override ValidationResult IsValid(object value, ValidationContext validationContext)
{
var _localizationService = (IStringLocalizer<CustomDate>)validationContext.GetService(typeof(IStringLocalizer<CustomDate>));
if ((DateTime)value > DateTime.Now)
return new ValidationResult(_localizationService["Date of Birth cannot be in the future"]);
else if ((DateTime)value < new DateTime(1980, 1, 1))
return new ValidationResult(_localizationService["Date of Birth should not be before 1980"]);
return ValidationResult.Success;
}
}
}
Explanation: Here I used IStringLocalizer<T> object to fetch my culture-specific resources at run time. It is a service that provides localized strings stored in resource files.
var _localizationService = (IStringLocalizer<CustomDate>)validationContext.GetService(typeof(IStringLocalizer<CustomDate>));Notice how I am fetching the language specific strings from the resource file by the following codes:
_localizationService["Date of Birth cannot be in the future"]
(_localizationService["Date of Birth should not be before 1980"]Next, create 2 resource files in the same directory of the custom validation class (i.e. ‘Infrastructure’ folder) and name them as:
- CustomDate.es.resx
- CustomDate.fr.resx
Inside these resource files put the French and Spanish text for the string – ‘Date of Birth cannot be in the future’ & ‘Date of Birth should not be before 1980’.
| Name | Value |
|---|---|
| Date of Birth cannot be in the future | La fecha de nacimiento no puede ser en el futuro |
| Date of Birth should not be before 1980 | La fecha de nacimiento no debe ser anterior a 1980 |
| Name | Value |
|---|---|
| Date of Birth cannot be in the future | La date de naissance ne peut pas être dans le futur |
| Date of Birth should not be before 1980 | La date de naissance ne doit pas être antérieure à 1980 |
Controllers localization using Resource files
The controller has one action method which is called when the form is submitted. On successful submission I have to show success message in 3 languages (en, fr, es) based on the user’s culture.
First I have to inject IStringLocalizer object on the controller’s constructor using dependency injection feature of asp.net core, and then fetch the relevant culture specific string message from the resource file. This message is shown to the user on the form submission.
The controller’s code is given below:
public class HomeController : Controller
{
private readonly IStringLocalizer<HomeController> _localizer;
public HomeController(IStringLocalizer<HomeController> localizer)
{
_localizer = localizer;
}
public IActionResult Index()
{
return View();
}
[HttpPost]
public IActionResult Index(JobApplication jobApplication)
{
if (ModelState.IsValid)
ViewBag.Message = _localizer["Your application is accepted"];
return View();
}
}
ViewBag is filled with the localized message stored in the resource file from:
ViewBag.Message = _localizer["Your application is accepted"]The _localizer is the variable that contains IStringLocalizer object, and it’s task is to provide me with culture specific text stored in the resource file.
Next, create the 2 resource files inside the ‘Controllers’ folder and name them as:
- HomeController.es.resx
- HomeController.fr.resx
Note that HomeController.cs is the name of my controller file and this may be different in your case.
Since I am having only one string which is ‘Your application is accepted’, therefore both the resource files will have just one entry.
I have shown this in the below 2 images of the controller’s resource files:
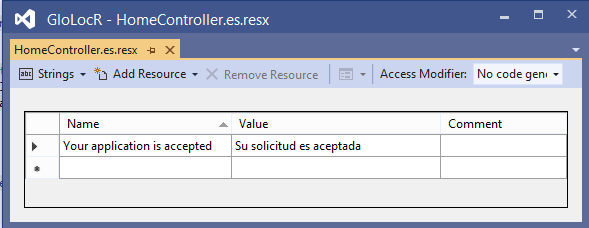
It’s enteries are:
| Name | Value |
|---|---|
| Your application is accepted | Su solicitud es aceptada |
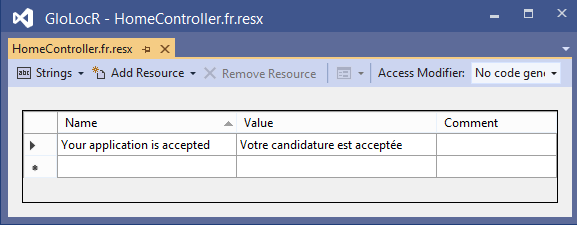
It’s enteries are:
| Name | Value |
|---|---|
| Your application is accepted | Votre candidature est acceptée |
Views localization using Resource files
The IViewLocalizer service provides localized strings for a view and to use it you have to inject in your View as shown below:
@inject IViewLocalizer LocalizerThe Job Application form resides in my Index.cshtml razor view file and it may be different in your case. So first add the necessary namespace in your View:
@using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Builder
@using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Localization
@using Microsoft.Extensions.Options
@using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc.Localization Then inject IViewLocalizer & IOptions
@inject IViewLocalizer Localizer
@inject IOptions<RequestLocalizationOptions> LocOptionsThrough the RequestLocalizationOptions object I will fill a select control with the cultures that the website will support. This will also help user to select their culture and the form will be presented based on the selected culture of the user.
Now add the below code that will create and fill the select control’s options.
@{
var requestCulture = Context.Features.Get<IRequestCultureFeature>();
var cultureItems = LocOptions.Value.SupportedUICultures
.Select(c => new SelectListItem { Value = c.Name, Text = c.DisplayName })
.ToList();
}
<label>Language:</label>
<select onchange="SetCulture(this.value)" asp-for="@requestCulture.RequestCulture.UICulture.Name" asp-items="cultureItems">
</select>A bit of JavaScript code will be needed to redirect the users to their selected culture based job application form. This JS code which you will add to the view is given below:
<script>
function SetCulture(selectedValue) {
var url = window.location.href.split('?')[0];
var culture = "?culture=" + selectedValue + "&ui-culture=" + selectedValue;
window.location.href = url + culture;
}
</script>Here I am using QueryStringRequestCultureProvider where the culture which is selected by the user is added to the query string of the url. So the French version of the application form will have the url given by:
https://localhost:44356/?culture=fr&ui-culture=frWhile the Spanish version of the form will have the url as:
https://localhost:44356/?culture=es&ui-culture=esThe English version does not need to add the culture in the query string so the form’s url will be:
https://localhost:44356Next all you have to do is put the form in the View. The full code of the Index.cshtml view file is given below:
@{
ViewData["Title"] = "Home Page";
}
<div class="text-center">
<h1 class="display-4">@Localizer["Welcome"]</h1>
<p>@Localizer["Learn about"] <a href="https://www.yogihosting.com">@Localizer["building Web apps with ASP.NET Core"]</a>.</p>
</div>
@using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Builder
@using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Localization
@using Microsoft.Extensions.Options
@using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc.Localization
@inject IViewLocalizer Localizer
@inject IOptions<RequestLocalizationOptions> LocOptions
@{
var requestCulture = Context.Features.Get<IRequestCultureFeature>();
var cultureItems = LocOptions.Value.SupportedUICultures
.Select(c => new SelectListItem { Value = c.Name, Text = c.DisplayName })
.ToList();
}
<label>Language:</label>
<select onchange="SetCulture(this.value)" asp-for="@requestCulture.RequestCulture.UICulture.Name" asp-items="cultureItems">
</select>
@model JobApplication
<h2>@Localizer["Job Application"]</h2>
<h3 class="alert-danger">@ViewBag.Message</h3>
<div asp-validation-summary="All" class="text-danger"></div>
@{
string culture = "", uiculture = "";
if (Context.Request.QueryString.HasValue)
{
string url = Context.Request.QueryString.Value;
culture = Context.Request.Query["culture"];
uiculture = Context.Request.Query["ui-culture"];
}
}
<form class="m-1 p-1" asp-action="Index" asp-route-culture="@culture" asp-route-ui-culture="@uiculture" method="post">
<div class="form-group">
<label asp-for="Name"></label>
<input asp-for="Name" class="form-control" />
<span asp-validation-for="Name" class="text-danger"></span>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label asp-for="DOB"></label>
<input asp-for="DOB" type="text" asp-format="{0:d}" class="form-control" />
<span asp-validation-for="DOB" class="text-danger"></span>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label asp-for="Sex"></label>
<div>
<input asp-for="Sex" type="radio" value="M" />@Localizer["Male"]
<input asp-for="Sex" type="radio" value="F" />@Localizer["Female"]
</div>
<span asp-validation-for="Sex" class="text-danger"></span>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label asp-for="Experience"></label>
<select asp-for="Experience" class="form-control">
<option value="Select">@Localizer["Select"]</option>
<option value="0">Fresher</option>
<option value="1">0-1 years</option>
<option value="2">1-2 years</option>
<option value="3">2-3 years</option>
<option value="4">3-4 years</option>
<option value="5">4-5 years</option>
</select>
<span asp-validation-for="Experience" class="text-danger"></span>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<input asp-for="TermsAccepted" />
<label asp-for="TermsAccepted" class="form-check-label">
@Localizer["I accept the terms & conditions"]
</label>
<span asp-validation-for="TermsAccepted" class="text-danger"></span>
</div>
<button name="formsubmit" value="Button Control" type="submit" class="btn btn-primary">@Localizer["Submit Application"]</button>
</form>
<script>
function SetCulture(selectedValue) {
var url = window.location.href.split('?')[0];
var culture = "?culture=" + selectedValue + "&ui-culture=" + selectedValue;
window.location.href = url + culture;
}
</script>
Explanation : The data annotations messages will come from the model resources file which I explained in the earlier part. For the other string of the view the culture related strings are fetched from the ‘IViewLocalizer’ by using the code – @Localizer["SomeString"].
See the radio button code where I did this thing:
<input asp-for="Sex" type="radio" value="M" />@Localizer["Male"]
<input asp-for="Sex" type="radio" value="F" />@Localizer["Female"]Similarly the terms label is doing the same thing:
<label asp-for="TermsAccepted" class="form-check-label">
@Localizer["I accept the terms & conditions"]
</label>Next create 2 resource file in the same direction of the view. In my case it is Views ➤ Home directory. Name these 2 resource files as:
- Index.es.resx
- Index.fr.resx
Add the necessary string and there Spanish & French texts in these files which are given below:
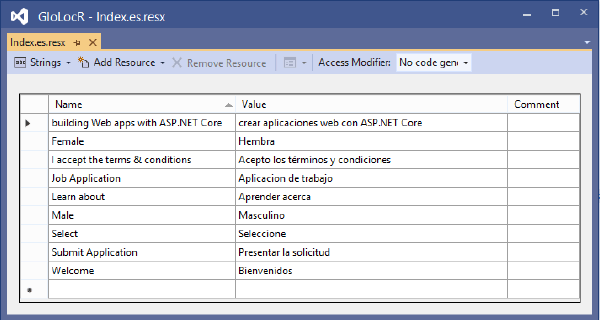
It’s enteries are given below:
| Name | Value |
|---|---|
| building Web apps with ASP.NET Core | crear aplicaciones web con ASP.NET Core |
| Female | Hembra |
| I accept the terms & conditions | Acepto los términos y condiciones |
| Job Application | Aplicacion de trabajo |
| Learn about | Aprender acerca |
| Male | Masculino |
| Select | Seleccione |
| Submit Application | Presentar la solicitud |
| Welcome | Bienvenidos |
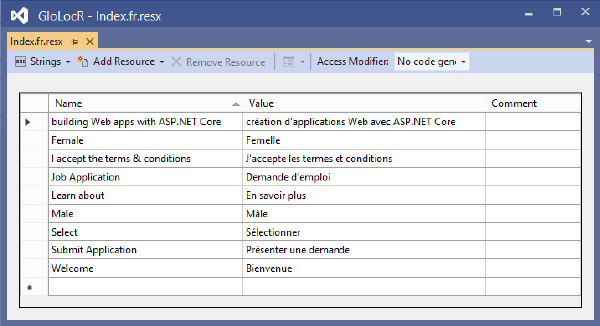
It’s enteries are:
| Name | Value |
|---|---|
| building Web apps with ASP.NET Core | création d’applications Web avec ASP.NET Core |
| Female | Femelle |
| I accept the terms & conditions | J’accepte les termes et conditions |
| Job Application | Demande d’emploi |
| Learn about | En savoir plus |
| Male | Mâle |
| Select | Sélectionner |
| Submit Application | Présenter une demande |
| Welcome | Bienvenue |
Let’s test how it all works. I have shown these in 2 videos, the first one showing the user selecting his culture and the relevant form version showing up in the browser.
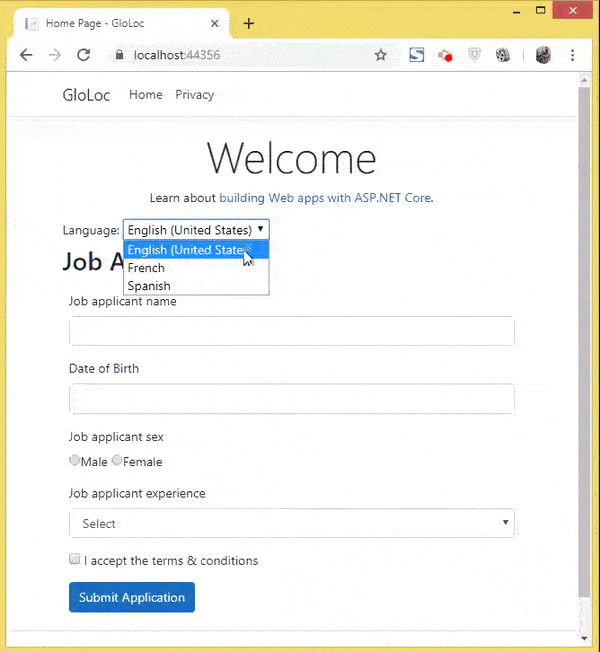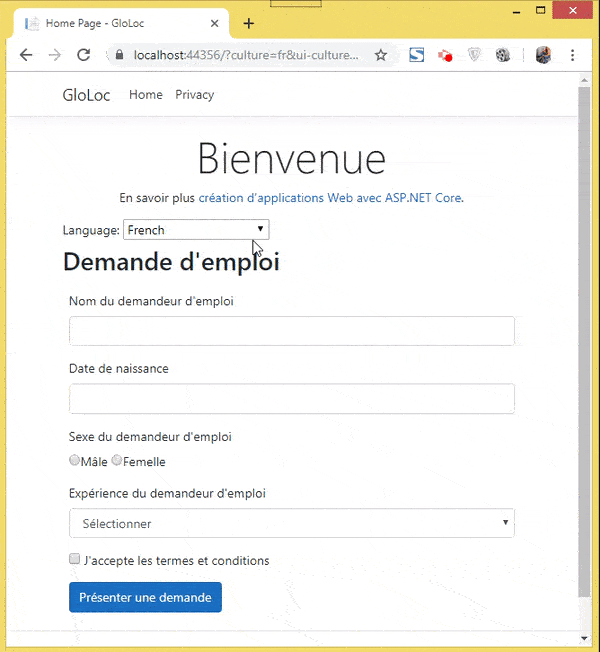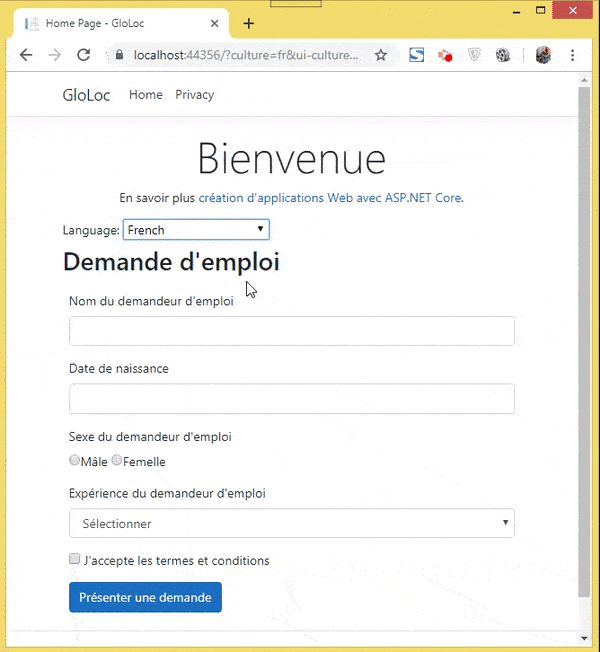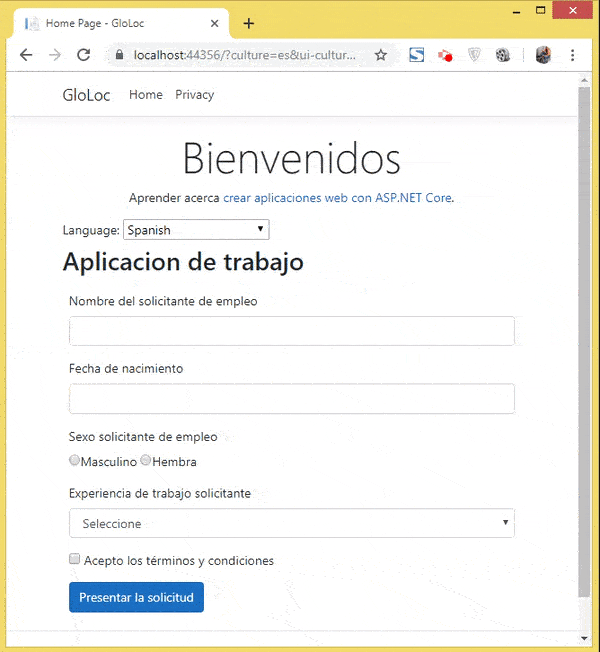
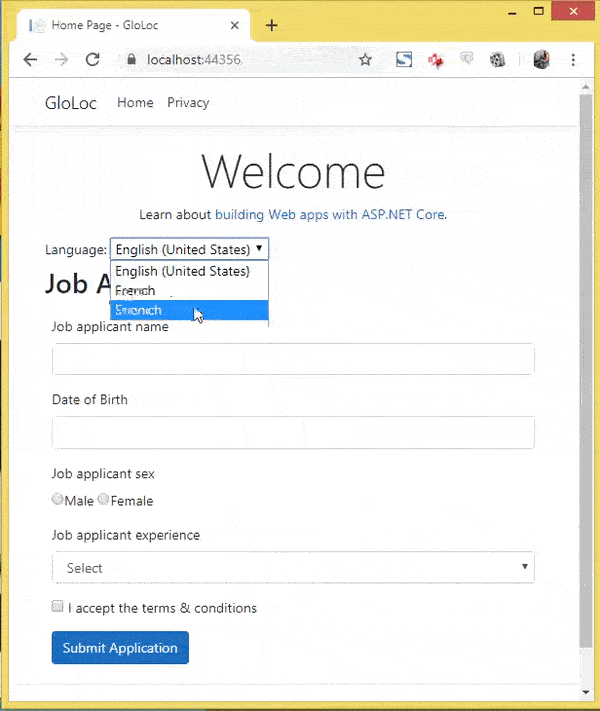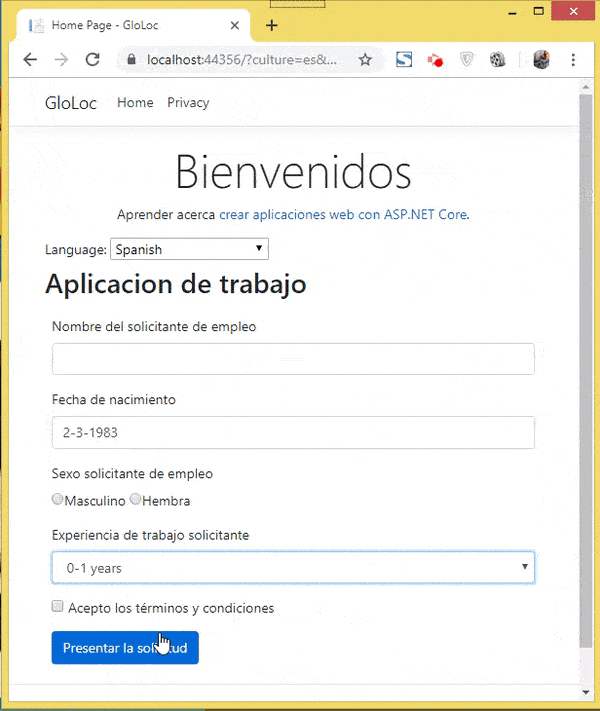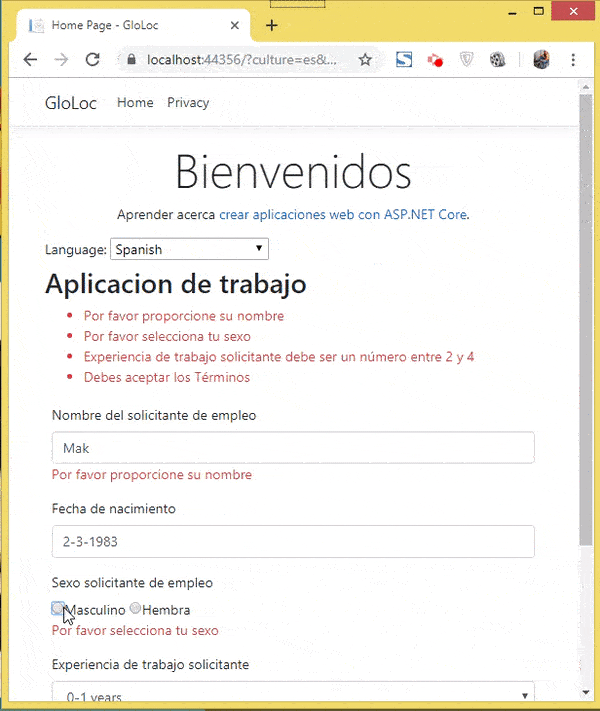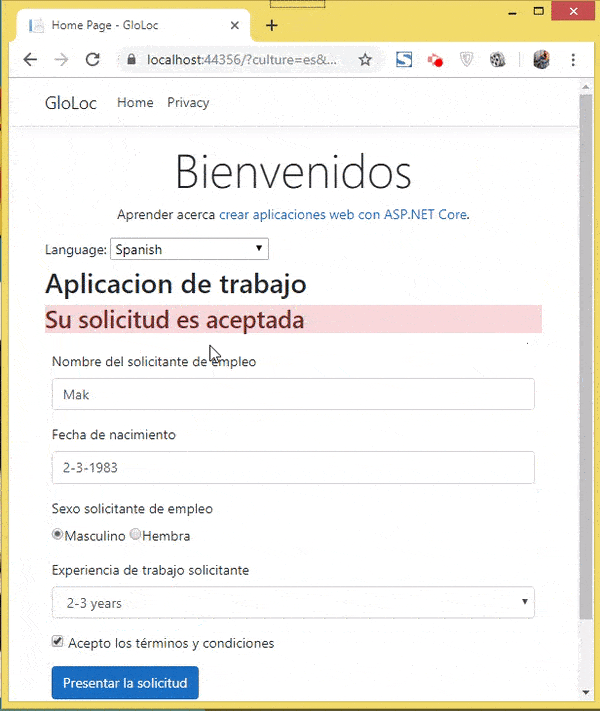
The next video shown the data annotation messages in Spanish & French version.
You can download the full source code by clicking the below link:
Resource files location
You can also change resource files location by adding the following code in Program class.
builder.Services.AddLocalization(options => options.ResourcesPath = "Resources");Here I have set the ‘Resources’ folder, which is located on the root of the website, to contain all the resources files.
So in this case the resource file for HomeController should be located on any of the 2 locations:
1. Inside the Resources/Controllers/ folder as:
- Resources/Controllers/HomeController.es.resx
- Resources/Controllers/HomeController.fr.resx
2. Inside the Resources folder as:
- Resources/Controllers.HomeController.es.resx
- Resources/Controllers.HomeController.fr.resx
The resources files for data annotations should be located in:
- Resources/Models.JobApplication.es.resx
- Resources/Models.JobApplication.fr.resx
Or
- Resources/Models/JobApplication.es.resx
- Resources/Models/JobApplication.fr.resx
The resource files for the View should be located in:
- Resources/Views.Home.Index.es.resx
- Resources/Views.Home.Index.fr.resx
Or
- Resources/Views/Home/Index.es.resx
- Resources/Views/Home/Index.fr.resx
This tutorial looked at how to use resource files as part of localising the content of an asp.net core website.
Resource files were made for a specific page, and for more general use around the site. I also explained the naming of these resource file and where you need to place them.
I hoped you enjoyed reading as much as I enjoyed creating this long tutorial.







 Welcome to YogiHosting - A Programming Tutorial Website. It is used by millions of people around the world to learn and explore about ASP.NET Core, Blazor, jQuery, JavaScript, Docker, Kubernetes and other topics.
Welcome to YogiHosting - A Programming Tutorial Website. It is used by millions of people around the world to learn and explore about ASP.NET Core, Blazor, jQuery, JavaScript, Docker, Kubernetes and other topics.