Configure One-to-Many relationship using Fluent API in Entity Framework Core
Entity Framework Core One-to-Many Relationship is established between 2 entities by the use of Fluent APIs. This relationship is configured by the use of Has/With pattern.
The Has side of the pattern has 2 variants which are HasOne() and HasMany() methods. The With side of the pattern has 2 variants which are WithOne() and WithMany() methods. We can use either one from the below 2 Has/With patterns to create a relationship.
- HasOne – WithMany
- HasMany – WithOne
Page Contents
Example: Fluent API One-to-Many Relationship
Consider the following Country and City entities.
public class Country
{
public int Id { get; set; }
public string Name { get; set; }
public ICollection<City> City { get; } = new List<City>();
}
public class City
{
public int Id { get; set; }
public string Name { get; set; }
public int FKCountry { get; set; }
public Country Country { get; set; } = null!;
}
The Country entity has a Collection Navigation Property called City.
public ICollection<City> City { get; } = new List<City>();The City entity has a Reference Navigation Property called Country.
public Country Country { get; set; } = null!;Since the references are discovered though Conventions therefore Entity Framework Core will create one-to-many relationship between these 2 entities automatically. We have seen this in our previous tutorial – Entity Framework Core One-to-Many Relationship through Conventions.
For cases where the navigations, foreign key, suggesting the relationship are not discovered by convention, these things can be configured explicitly by the help of Fluent APIS.
So let’s create the Entity Framework Core One-to-Many Relationship with Fluent API for these 2 entities by overriding the OnModelCreating method in the Database Context class, as shown below.
public class CountryContext: DbContext
{
public DbSet<City> City { get; set; }
public DbSet<Country> Country { get; set; }
public CountryContext(DbContextOptions<CountryContext> options) : base(options)
{
}
protected override void OnModelCreating(ModelBuilder modelBuilder)
{
//Write Fluent API configurations here
modelBuilder.Entity<City>()
.HasOne(e => e.Country)
.WithMany(e => e.City)
.HasForeignKey(e => e.FKCountry)
.IsRequired();
}
}
On performing EF Core Migrations we will get Country and City database tables created having foreign key as FKCountry on the City table.
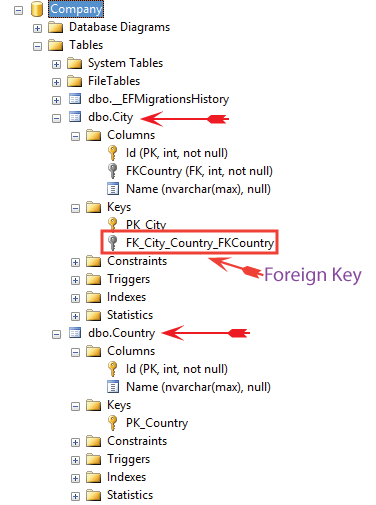
Understanding One-to-Many Relationship Configuration
- We can start by configuring any one entity (either Country or City class). Here we start with City entity class by saying modelBuilder.Entity<City>).
- Next, we use the Has/With pattern, by using the .HasOne(e => e.Country) method, we specified that the city entity contains the reference navigation property of other type “Country”. This creates the one-to-many relationship between them.
- Next, we move to the other end of the relationship, and by using the .WithMany(e => e.City) method we specified that the Country entity includes collection navigation property of the City type.
- The .HasForeignKey(e => e.FKCountry) specifies that the property called FKCountry is the foreign key for the City table in the database.
- The .IsRequired() make this relationship as required. This means the foreign key cannot be null. If we want to allow null for foreign key then use .IsRequired(false).
You can also configure the same One-to-Many Relationship by using the HasMany – WithOne pattern. So in this case we start with Country entity and then create this relationship as shown by the below code:
modelBuilder.Entity<Country>()
.HasMany(e => e.City)
.WithOne(e=>e.Country)
.HasForeignKey(e => e.FKCountry)
.IsRequired();
Cascade Delete in Fluent API for Foreign Keys
EF Core behaves differently when the parent entity of the foreign key is deleted. We can configure this using Fluent API. We can instruct EF Core to delete the child row from the db table if the related parent row is deleted, or set foreign key to null, or prevent delete.
This is done from .OnDelete() method.
On the below code, we have set DeleteBehaviour as Cascade which means the dependent entity will be deleted when its parent entity is deleted.
modelBuilder.Entity<City>()
.HasOne(e => e.Country)
.WithMany(e => e.City)
.HasForeignKey(e => e.FKCountry)
.OnDelete(DeleteBehavior.Cascade); //Cascade behaviour
The DeleteBehaviour has 4 values:
- Cascade : Dependent entities will be deleted if its principal entity is deleted. This is the default behaviour and so we can omit OnDelete method.
- ClientSetNull: The values of foreign key properties in the dependent entities will be set to null when its parent entity is deleted.
- Restrict: Prevents Cascade delete. It will thow exception instead of automatically deleting dependent entities.
- SetNull: The values of foreign key properties in the dependent entities will be set to null when its parent entity is deleted.
Cascade delete Example
We have some names of Cities and Countries in the database tables, as shown by the below image.
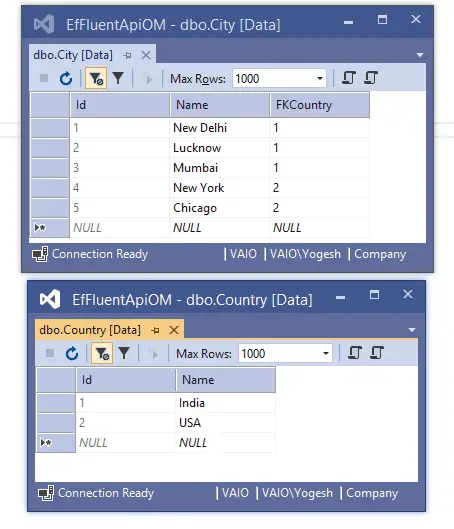
Now we will delete Country having an Id ‘1’ from the Country table using the below EF Core code:
Country country = new Country()
{
Id = 1
};
context.Remove(country);
await context.SaveChangesAsync();
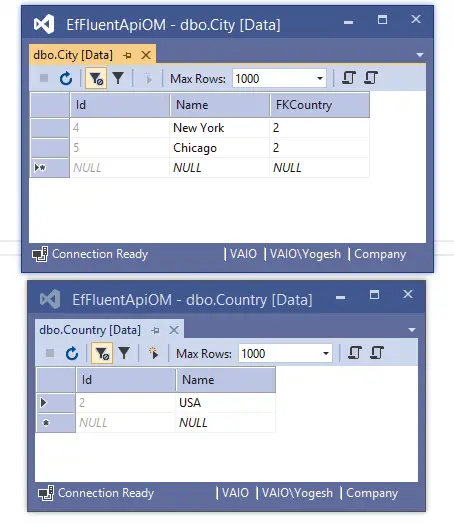
Since the configuration is set for Cascade Delete then all the cities associated with the country having id ‘1’ are also deleted automatically. See the below picture where we have shown the snapshot of the 2 tables after executing the delete. This proves the cascade delete is working properly.
Shadow Properties
The properties which are defined in Entity Framework Core through Fluent APIs but are not defined in the Entity class are called Shadow Properties. Example we have a “Country.cs” entity class which have 2 properties Id and Name.
public class Country
{
public int Id { get; set; }
public string Name { get; set; }
}We can defined a shadow property called “Established” with Fluent API as shown below.
protected override void OnModelCreating(ModelBuilder modelBuilder)
{
modelBuilder.Entity<Country>()
.Property<DateTime>("Established");
}Shadow property can be accessed or changed through the ChangeTracker API. These properties can be referenced through LINQ queries via the EF.Property static method.
// ChangeTracker API to add a value to shadow property
context.Entry(myCountry).Property("Established").CurrentValue = DateTime.Now;
//Reference shadow property through LINQ queries via EF.Property
var countries = context.Country
.OrderBy(b => EF.Property<DateTime>(b, "Established"));Shadow properties are useful when there’s data in the database that shouldn’t be exposed on the mapped entity types. The value and state of these properties are maintained purely in the Change Tracker.
Foreign key Shadow Properties
Shadow properties are also used for foreign key properties. When we don’t define a foreign key property (by convention or explicitly) then EF Core automatically adds them. Consider the below 2 entities having foreign key relationships.
public class Country
{
public int Id { get; set; }
public string Name { get; set; }
public ICollection<City> City { get; } = new List<City>();
}
public class City
{
public int Id { get; set; }
public string Name { get; set; }
public Country Country { get; set; }
}In the Country entity we haven’t defined foreign key property given below.
public int FKCountry { get; set; }So here EF Core will add the shodow property and the value for the foreign key column is stored in the corresponding shadow property. That is a property called “CountryId”, which is the shadow property is introduced, to the Country entity.
A shadow foreign key will also be created if the argument to “HasForeignKey” does not match any .NET property. In the below example EF Core will make MyFrKey the shadow foreign key.
protected override void OnModelCreating(ModelBuilder modelBuilder)
{
modelBuilder.Entity<Country>()
.HasMany(e => e.City)
.WithOne(e => e.Country)
.HasForeignKey("MyFrKey");
}One-to-many with Alternate Key
An Alternate Key is a secondary key that is capable of identifying a row uniquely. Suppose our database table also has an Alternate Key then we can configure it through Fluent APIs.
public class Country
{
public int Id { get; set; }
public string Name { get; set; }
public int AlternateId { get; set; } // Alternate key
public ICollection<City> City { get; } = new List<City>();
}
public class City
{
public int Id { get; set; }
public string Name { get; set; }
public int FKCountry { get; set; }
public Country Country { get; set; } = null!;
}
Alternate key is configured explicitly in OnModelCreating using a call to HasPrincipalKey method.
protected override void OnModelCreating(ModelBuilder modelBuilder)
{
//Write Fluent API configurations here
modelBuilder.Entity<City>()
.HasOne(e => e.Country)
.WithMany(e => e.City)
.HasPrincipalKey(e => e.AlternateId)
.HasForeignKey(e => e.FKCountry)
.IsRequired();
}
One-to-many with Composite Keys
Let’s discuss how to configure composite keys. The Country entity has 2 properties “Id1” and “Id2” forming the composite keys. For the City entity we need to have not 1 but 2 foreign keys because when the principal of a relationship has a composite key, then the foreign key of the dependent must also be a composite key with the same number of properties.
The code is given below.
public class Country
{
public int Id1 { get; set; } // Composite key part 1
public int Id2 { get; set; } // Composite key part 2
public string Name { get; set; }
public ICollection<City> City { get; } = new List<City>();
}
public class City
{
public int Id { get; set; }
public string Name { get; set; }
public int FKCountry1 { get; set; } // Required foreign key property part 1
public int FKCountry2 { get; set; } // Required foreign key property part 2
public Country Country { get; set; } = null!;
}
With .HasKey() method we can configure the Composite keys as shown below.
modelBuilder.Entity<Country>()
.HasKey(e => new { e.Id1, e.Id2 });The other part of the configuration to specify keys with multiple properties is given below.
modelBuilder.Entity<City>()
.HasOne(e => e.Country)
.WithMany(e => e.City)
.HasPrincipalKey(e => new { e.Id1, e.Id2 })
.HasForeignKey(e => new { e.FKCountry1, e.FKCountry2 })
.IsRequired();Self-referencing one-to-many
Suppose the principal and dependent entities are not different but same. In this case also we can configure them with Fluent apis. In the below example we have only one entity which is an Employee entity whose code is given below.
public class Employee
{
public int Id { get; set; }
public int? ManagerId { get; set; } // Optional foreign key property
public Employee? Manager { get; set; } // Optional reference navigation to principal
public ICollection<Employee> Reports { get; } = new List<Employee>(); // Collection navigation containing dependents
} An employee can be a manager or can have a manager which is represented by “ManagerId” property. This property forms the optional foreign key. The “Manager” property is the refrence navigation property of optional type. The property “Reports” is the collection navigation property.
We can configure it as shown below.
protected override void OnModelCreating(ModelBuilder modelBuilder)
{
modelBuilder.Entity<Employee>()
.HasOne(e => e.Manager)
.WithMany(e => e.Reports)
.HasForeignKey(e => e.ManagerId)
.IsRequired(false);
}
Foreign key Constraint Names
In the database the foreign key constraints are named by EF Core as – FK_<dependent type name>_<principal type name>_<foreign key property name>. For composite foreign keys it is named as <foreign key property name1_foreign key property name2>.
The name can be changed by using Fluent API as:
protected override void OnModelCreating(ModelBuilder modelBuilder)
{
modelBuilder.Entity<City>()
.HasOne(e => e.Country)
.WithMany(e => e.City)
.HasForeignKey(e => e.FKCountry)
.HasConstraintName("MyConstraint");
}Download the source code:








 Welcome to YogiHosting - A Programming Tutorial Website. It is used by millions of people around the world to learn and explore about ASP.NET Core, Blazor, jQuery, JavaScript, Docker, Kubernetes and other topics.
Welcome to YogiHosting - A Programming Tutorial Website. It is used by millions of people around the world to learn and explore about ASP.NET Core, Blazor, jQuery, JavaScript, Docker, Kubernetes and other topics.