Conventions in Entity Framework Core
Entity Framework Core Conventions are default rules by which the Database Schema is created based on Domain classes and DbContext. For example – the table names, column names, relationships, primary & foreign keys are all created based on these conventions.
Page Contents
Example of Entity Framework Core Conventions
Let us understand conventions with an example. We have a project containing the following 2 domain classes (i.e. entities), these are Employee and Department.
public class Employee
{
public int Id { get; set; }
public int DepartmentId { get; set; }
public string Name { get; set; }
public string Designation { get; set; }
public Department Department { get; set; }
}
public class Department
{
public int Id { get; set; }
public string Name { get; set; }
public ICollection<Employee> Employee { get; set; }
}
The Database Context for the project is given below.
public class CompanyContext : DbContext
{
public CompanyContext(DbContextOptions<CompanyContext> options) : base(options)
{
}
public DbSet<Employee> Employee { get; set; }
}We all know that when we run Entity Framework Core migrations then the database will be created with 2 tables – Employee and Department. The conventions will be responsible for creation of the database schemas which are the tables, columns, relationships and so on. Let us look each of them one by one.
Table
The Entity Framework Core Conventions will create the database table is such a way that their names are the same as the DbSet<T> property names defined on the database context.
We have only one DbSet property which is named “Employee” – public DbSet<Employee> Employee { get; set; }. So EF Core will create a database table by the same name i.e. Employee. If we want a differnt name then we can change the name of this property.
This is all simple, but how the second table i.e. Department is created since we haven’t defined a DbSet for it. The answer is Entity Framework Core will also create tables for the domain classes that are not included as DbSet properties but are reachable through Reference Navigation Properties given on other domain class.
In the Employee class we have defined a Reference Navigation Property – public Department Department { get; set; }. Through this property Entity Framework Core finds the “Department” entity and so it also creates a Table for it in the database.
Column
Entity Framework Core Conventions creates columns in the database table for all the scalar properties defined in the domain classes. The column names are kept the same as the property name. The Employee class has 4 scalar properties (Id, DepartmentId, Name, Designation) so 4 columns with the same names are created in the Employee table.
Similarly 2 columns with the names Id & Name will be created in the Department table.
Reference and collection properties are used to create relationships between the tables. We will see this in just a moment.
C# data type to SQL Server column data type
The next thing which comes to your mind is how EF Core decides what data types the columns of the database tables will have. This is done by the fixed mapping rules of C# data types to SQL Server database, see below.
| C# Data Type | Mapping to SQL Server Data Type |
|---|---|
| int | int |
| string | nvarchar(Max) |
| decimal | decimal(18,2) |
| float | real |
| bool | bit |
| long | bigint() |
| datetime | datetime |
| short | smallint |
Based on the mapping rules the columns of the 2 tables in our case are:
// Department table
Id INT IDENTITY (1, 1) NOT NULL
Name VARCHAR (50) NOT NULL
// Employee table
Id INT IDENTITY (1, 1) NOT NULL
DepartmentId INT NOT NULL
Name VARCHAR (100) NOT NULL
Designation VARCHAR (25) NOT NULL
Nullable Column
Null columns are created for all reference data types and nullable primitive type properties like string?, Nullable, float?.
NotNull Column
Entity Framework Core will create NotNull columns in the database tables for primary key properties and primitive type properties like string, float, int, DateTime.
Primary Key
The EF Core creates the primary key for a database table for the C# property which is named Id or contains “id” text (case insensitive).
For the Employee table the EF Core will create primary key if the Employee domain class includes a property named id, ID, iD, Id, employeeid, EmployeeId, EMPLOYEEID, EmPLoyEEid, etc. For our case “Id” is the primary key for Employee table and “Id” is the primary key for Department table.
Foreign Key
The Entity Framework Core Conventions will create foreign key column for each reference navigation property in the domain class. In our case, for ‘Employee’ & ‘Department’ domain classes, it will create foreign key column called DepartmentId in the Employee table.
Also note that their is One-to-Many Relationship between these 2 entities. That is one Department can contain many Employees and vice versa.
Database Tables Relationships
The tables of a Relational Database like SQL Server can have 3 types of relationship between them.
- One-to-Many Relationship
- One-to-One Relationship
- Many-to-Many Relationship
Let’s see how Entity Framework Core Conventions does this.
One-to-Many Relationship
We will learn how to apply One-to-Many Relationship between domain classes in Entity Framework Core. Suppose we have 2 database tables – Country & City. We all know there can be many cities in a single country. Which means we can create One-to-Many relationship between these 2 tables.
Start by adding 2 Classes for Country & City. We have shown this below.
public class Country
{
public int Id { get; set; }
public string Name { get; set; }
}
public class City
{
public int Id { get; set; }
public string Name { get; set; }
}
To create a Many-to-One relationship between these 2 classes we can follow 4 conventions. These conventions are listed below:
On the City class create a reference navigation property pointing to the Country class as shown below:
public class City
{
public int Id { get; set; }
public string Name { get; set; }
public Country Country { get; set; } //Reference Navigation Property
}
public class Country
{
public int Id { get; set; }
public string Name { get; set; }
}
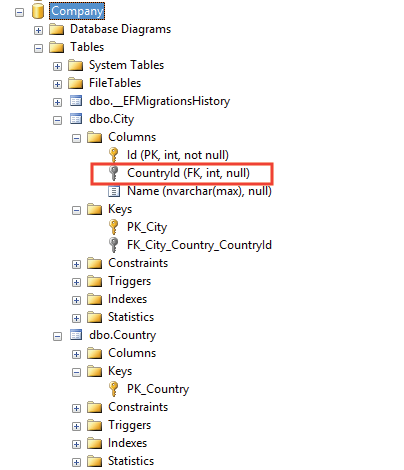
On applying the EF Core Migrations it will produce a one-to-many relationship (foreign key) between the City and Country tables in the database, where City table includes a nullable foreign key called ‘CountryId’, as shown by the image given below.
Another way to create one-to-many relationship is by adding Collection Navigation Property i.e. by adding ICollection type property in the Country class as shown below.
public class City
{
public int Id { get; set; }
public string Name { get; set; }
}
public class Country
{
public int Id { get; set; }
public string Name { get; set; }
public ICollection<City> Cities { get; set; } // Collection Navigation Property
}
This will do the same work as the Convention 1 when we apply migrations.
We can also create both Reference & Collection Navigation Properties on the entities to create foreign key relationship (One-to-Many).
public class City
{
public int Id { get; set; }
public string Name { get; set; }
public Country Country { get; set; } //Reference Navigation Property
}
public class Country
{
public int Id { get; set; }
public string Name { get; set; }
public ICollection<City> Cities { get; set; } // Collection Navigation Property
}
One the above code see that we have added Reference Navigation Property on the City entity, and Collection Navigation Property on the Country entity.
In this case we use the Convention 3 and also add a foreign key property CountryId of type int on the City entity.
public class City
{
public int Id { get; set; }
public string Name { get; set; }
public int CountryId { get; set; } //Foreign Key entity
public Country Country { get; set; } //Reference Navigation Property
}
public class Country
{
public int Id { get; set; }
public string Name { get; set; }
public ICollection<City> Cities { get; set; } // Collection Navigation Property
}
One-to-One Relationship
Creating One-to-One relationship between entity classes is very simple in Entity Framework Core. All we have to do is add Reference Navigation properties on both the entities.
In the below code I have created One-to-One Relationship between the ‘Country’ & ‘City’ entity classes.
public class City
{
public int Id { get; set; }
public string Name { get; set; }
public Country Country { get; set; } //Reference Navigation Property
}
public class Country
{
public int Id { get; set; }
public string Name { get; set; }
public City City { get; set; } //Reference Navigation Property
}
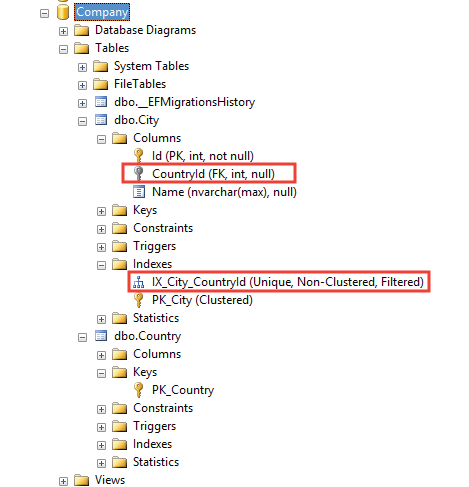
We have shown this on the below image:
Many-to-Many Relationship
To establish Many-to-Many Relationship between entities we have to include collection navigation property on both sides.
public class City
{
public int Id { get; set; }
public string Name { get; set; }
public ICollection<Country> Country { get; set; } //Collection Navigation Property
}
public class Country
{
public int Id { get; set; }
public string Name { get; set; }
public ICollection<City> City { get; set; } //Collection Navigation Property
}
This will be implemented by adding a new join table on the database called CityCountry in our case. This table will contain foreign keys for both City and Country tables. This topic is covered in more details at Configure Many-to-Many relationship using Fluent API in Entity Framework Core, so do check it.








 Welcome to YogiHosting - A Programming Tutorial Website. It is used by millions of people around the world to learn and explore about ASP.NET Core, Blazor, jQuery, JavaScript, Docker, Kubernetes and other topics.
Welcome to YogiHosting - A Programming Tutorial Website. It is used by millions of people around the world to learn and explore about ASP.NET Core, Blazor, jQuery, JavaScript, Docker, Kubernetes and other topics.